Eco-Everest: Protecting the Environment
Our focus will be on climbing in an eco-sensitive manner, bringing all garbage and all human waste produced on the mountain down to base camp for proper disposal. We will be using highly successful alternative energy solutions like the parabolic solar cookers and the SteriPENs for water purification as well as solar panels to recharge batteries for radios, cameras, satellite phones, GPS’s and other electronic equipment. In all our climbs we adopt “Leave No Trace®” practices.
|
Our goal is to bring 400 lbs of existing garbage back (old ropes, tents, abandoned climbing material, cans and organic waste) and 50 used and rusted oxygen bottles (they lay at 8,000 meters!) back for recycling. The cost of that cleaning is around $70,000. Also we plan to spend a few days in several Nepali villages distributing brochures with information about good environmental practices, the importance of clean, safe water and basic information about food related illnesses. The Doctor of the Extreme Everest Team will provide information and educational materials at the village's schools.
To participate in support of this Everest Expedition, you may choose one of the following:
|
Climbing Route Description - Nepal, Himalaya
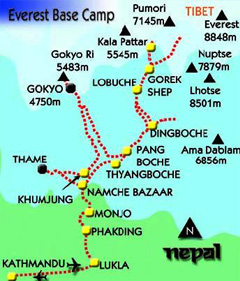
The ascent via the southeast ridge begins with a trek to Base Camp at 5,380 m (17,600 ft) on the south side of Everest in Nepal. The Expeditions will fly into Lukla (2,860 m) from Kathmandu and pass through Namche Bazaar. Climbers then hike to Base Camp, which usually takes six to eight days, allowing for proper altitude acclimatization in order to prevent altitude sickness. Climbing equipment and supplies are carried by yaks and human porters to Base Camp on the Khumbu Glacier.
Climbers will spend a couple of weeks in Base Camp, acclimatizing to the altitude. During that time, Sherpas and expedition climbers will set up ropes and ladders in the treacherous Khumbu Icefall. Seracs, crevasses and shifting blocks of ice make the icefall one of the most dangerous sections of the route. Many climbers and Sherpas have been killed in this section. To reduce the hazard, climbers will usually begin their ascent well before dawn when the freezing temperatures glue ice blocks in place. Above the icefall is Camp I or Advanced Base Camp (ABC) at 6,065 m (19,900 ft).
From Camp I, climbers make their way up the Western Cwm to the base of the Lhotse face, where Camp II is established at 6,500 m (21,300 ft). The Western Cwm is a relatively flat, gently rising glacial valley, marked by huge lateral crevasses in the centre which prevent direct access to the upper reaches of the Cwm. Climbers are forced to cross on the far right near the base of Nuptse to a small passageway known as the "Nuptse corner". The Western Cwm is also called the "Valley of Silence" as the topography of the area generally cuts off wind from the climbing route. The high altitude and a clear, windless day can make the Western Cwm unbearably hot for climbers.
From Camp II, climbers ascend the Lhotse face on fixed ropes up to Camp III, located on a small ledge at 7,470 m (24,500 ft). From there, it is another 500 metres to Camp IV on the South Col of Everest at 7,920 m (26,000 ft). From Camp III to Camp IV, climbers are faced with two additional challenges: The Geneva Spur and The Yellow Band. The Geneva Spur is an anvil shaped rib of black rock named by a 1952 Swiss expedition. Fixed ropes assist climbers in scrambling over this snow covered rock band. The Yellow Band is a section of sedimentary sandstone which also requires about 100 metres of rope for traversing it.
Climbers will spend a couple of weeks in Base Camp, acclimatizing to the altitude. During that time, Sherpas and expedition climbers will set up ropes and ladders in the treacherous Khumbu Icefall. Seracs, crevasses and shifting blocks of ice make the icefall one of the most dangerous sections of the route. Many climbers and Sherpas have been killed in this section. To reduce the hazard, climbers will usually begin their ascent well before dawn when the freezing temperatures glue ice blocks in place. Above the icefall is Camp I or Advanced Base Camp (ABC) at 6,065 m (19,900 ft).
From Camp I, climbers make their way up the Western Cwm to the base of the Lhotse face, where Camp II is established at 6,500 m (21,300 ft). The Western Cwm is a relatively flat, gently rising glacial valley, marked by huge lateral crevasses in the centre which prevent direct access to the upper reaches of the Cwm. Climbers are forced to cross on the far right near the base of Nuptse to a small passageway known as the "Nuptse corner". The Western Cwm is also called the "Valley of Silence" as the topography of the area generally cuts off wind from the climbing route. The high altitude and a clear, windless day can make the Western Cwm unbearably hot for climbers.
From Camp II, climbers ascend the Lhotse face on fixed ropes up to Camp III, located on a small ledge at 7,470 m (24,500 ft). From there, it is another 500 metres to Camp IV on the South Col of Everest at 7,920 m (26,000 ft). From Camp III to Camp IV, climbers are faced with two additional challenges: The Geneva Spur and The Yellow Band. The Geneva Spur is an anvil shaped rib of black rock named by a 1952 Swiss expedition. Fixed ropes assist climbers in scrambling over this snow covered rock band. The Yellow Band is a section of sedimentary sandstone which also requires about 100 metres of rope for traversing it.

On the South Col, climbers enter the Death Zone. Climbers typically only have a maximum of two or three days they can endure at this altitude for making summit bids. Clear weather and low winds are critical factors in deciding whether to make a summit attempt. If weather does not cooperate within these short few days, climbers are forced to descend, many all the way back down to Base Camp.
From Camp IV, climbers will begin their summit push around midnight with hopes of reaching the summit (still another 1,000 metres above) within 10 to 12 hours. Climbers will first reach "The Balcony" at 8,400 m (27,700 ft), a small platform where they can rest and gaze at peaks to the south and east in the early dawn light. Continuing up the ridge, climbers are then faced with a series of imposing rock steps which usually forces them to the east into waist deep snow, a serious avalanche hazard. At 8,750 m (28,700 ft), a small table-sized dome of ice and snow marks the South Summit.
From the South Summit, climbers follow the knife-edge southeast ridge along what is known as the "Cornice traverse" where snow clings to intermittent rock. This is the most exposed section of the climb as a misstep to the left would send one 2,400 m (8,000 ft) down the southwest face while to the immediate right is the 3,050 m (10,000 ft) Kangshung face. At the end of this traverse is an imposing 12 m (40 ft) rock wall called the "Hillary Step" at 8,760 m (28,750 ft).
From Camp IV, climbers will begin their summit push around midnight with hopes of reaching the summit (still another 1,000 metres above) within 10 to 12 hours. Climbers will first reach "The Balcony" at 8,400 m (27,700 ft), a small platform where they can rest and gaze at peaks to the south and east in the early dawn light. Continuing up the ridge, climbers are then faced with a series of imposing rock steps which usually forces them to the east into waist deep snow, a serious avalanche hazard. At 8,750 m (28,700 ft), a small table-sized dome of ice and snow marks the South Summit.
From the South Summit, climbers follow the knife-edge southeast ridge along what is known as the "Cornice traverse" where snow clings to intermittent rock. This is the most exposed section of the climb as a misstep to the left would send one 2,400 m (8,000 ft) down the southwest face while to the immediate right is the 3,050 m (10,000 ft) Kangshung face. At the end of this traverse is an imposing 12 m (40 ft) rock wall called the "Hillary Step" at 8,760 m (28,750 ft).

Sir Edmund Hillary and Sherpa Tenzing were the first climbers to ascend this step. Once above the step, it is a comparatively easy climb to the top on moderately angled snow slopes - though the exposure on the ridge is extreme especially while traversing very large cornices of snow. After the Hillary Step, climbers also must traverse a very loose and rocky section that has a very large entanglement of fixed ropes that can be troublesome in bad weather. Climbers will typically spend less than a half-hour on "top of the world" as they realize the need to descend to Camp IV before darkness sets in, afternoon weather becomes a serious problem, or supplemental oxygen tanks run out.
On the frequent clear days in April and May, the possibilities of spectacular photography and video recording are endless and they make exceptional marketing and promotion material for sponsors who support this adventure to the Ultimate Challenge: Climbing Mt Everest to the Top of the World!
On the frequent clear days in April and May, the possibilities of spectacular photography and video recording are endless and they make exceptional marketing and promotion material for sponsors who support this adventure to the Ultimate Challenge: Climbing Mt Everest to the Top of the World!






